Sistacircle: Every Tuesday At 1PM EST/10AM PST
What Does Nation Mean?
Just the word nation can raise strong sentiments, memories, impressions, and possibly conflicting ideas around who belongs where. "Nation" generally refers to a group of people who believe they belong to a shared cultural community with a common past and, according to Lina Sunseri, a shared orientation toward the future (2000). A "nation-state" is an independent and governed nation rooted in politics, border and territoriality; a "bounded community" (D'Arcangelis, 2010; Sunseri, 2000).
Patriotism and nationalism are intertwined with nation. According to the Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy, the standard (meaning man) dictionary definition of patriotism simply means "love of one's country" (2020), although patros, the root of patriotism, is not lost on feminists. According to Stephen Nathanson, a political scientist and man, patriotism involves a "special affection for one’s own country, a sense of personal identification with the country, special concern for the well-being of the country, and a willingness to sacrifice to promote the country’s good" (1993).
Commonly, nationalism can be thought of as what we believe about our nation, its history, nature, and value (Garner, 2022).
"At the heart of nationalism are claims about our identity and needs as social animals that form the basis of a series of normative claims" (Garner, 2022).
According to Annika Hamrud and Christina Wassholm, authors of Patriotism and Patriarchy: The impact of nationalism on gender equality, nationalism is, "...based on a trinity of people, family and homeland...[t]he hetero-sexual nuclear family with traditional gender roles forms the smallest unit of the nation. When the structure of the nuclear family is challenged, the nation is threatened by extension..." (2014, p.4). These statements mean family structures and the nation are male-dominated and interdependent.
Women in Canada
Canadian women, and women around the world, have a complicated relationship to nation and nation-state. Historically, women were denied the right to vote, own property, earn a fair wage and weren't even considered "persons" under Canadian law (Government of Canada, 2024). Indigenous women in Canada continue to endure the impacts of European male colonization which brought about the 1876 Indian Act, the Indian residential school system, and the reservation system (Smiley, 2023). These systems, and others within the patriarchy, continue to negatively impact the lives of Indigenous women and girls (Smiley, 2023). The relationship to nation and nation-state for Indigenous women in Canada, similar to other women, is marked by the ongoing fight for women's rights and an end to sex discrimination and male violence (Smiley, 2023).
Nationalism can be a source of solidarity and pride, but this issue of love and allegiance to country is also nuanced and complicated. The way women perceive nation could be described as a labyrinthine of perceptions and experiences marked by our herstory of exclusion as "persons" under the law and ongoing lack of self-determination as a sex class.

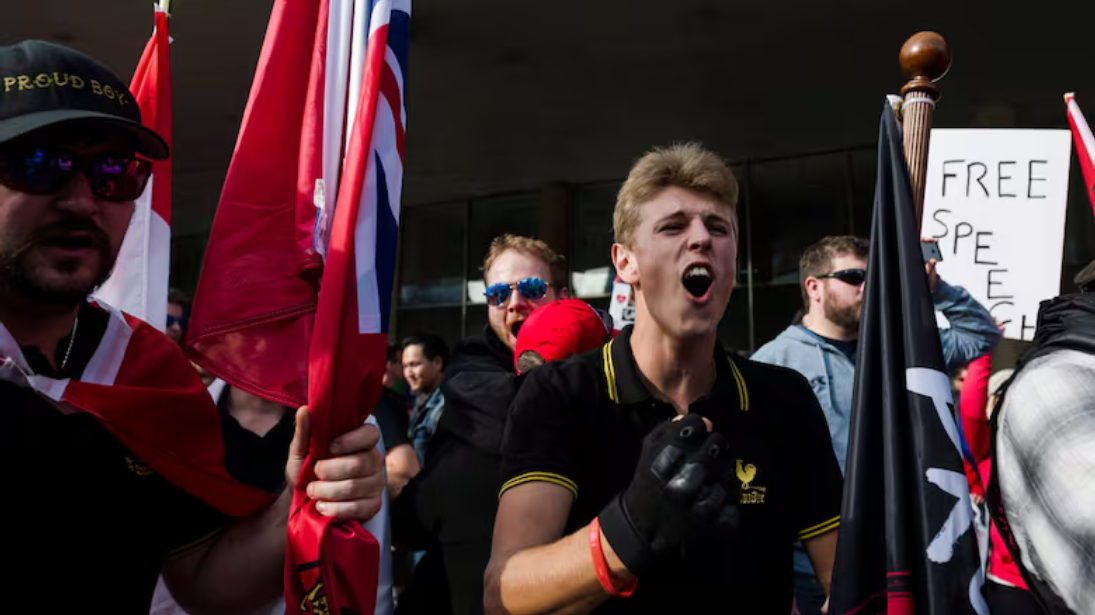
Is Nationalism And Far-Right Extremism Connected?
Many Canadians wear the maple leaf proudly and want to defend Canada's way of life and sovereignty. Patriotism can bring people together in times of celebration and hardship. However, some nationalist groups come together solely to oppose certain groups of people in Canada and this is when we see the intersection of patriarchy, racism, lesbophobia, and classism as national ideals (KC et al., 2021).
"...[Alt-right] belief systems come from a loose, heterogeneous collection of a wide range of grievances and positions, including racism; fascism; white supremacy/white nationalism; anti-Semitism; nativism/anti-immigration; anti-globalization/anti-free trade; anti-choice; homophobia; anti-taxation; and pro-militia/pro-gun rights stances... [a]s this list makes clear, the alt-right’s ideology spans multiple issues, but the central feature is power and white male domination" (KC et al., 2021, p. 3).

Questions To Consider
Do you believe women have a different connection to nation/nationalism than men do?
Are you able to describe your connection with your nation/nationalism?
What is your association with patriotism and does this align with your feminist values?